
一种新颖的整合进鱼骨状微混合器的分子印迹反蛋白石颗粒,用于高效、同时吸附多种生物分子。
Introduction
血液中过量的生物分子会不可避免地对肾脏造成损害,并可能导致许多疾病,如慢性肾病和尿毒症。移除这些生物分子对人类健康至关重要。为此,大量体外血液净化技术被开发,包括:物理吸附、血液透析、血液滤过和血浆置换等。这些方法显示出一定的去除能力,但也有局限性,如非特异性吸附和使用的透析/过滤材料的生物相容性差。相反,分子印迹通过一种锁与钥匙结构的分子结合机制提供了一种化学特异性识别过程,可以作为一种可替代的方法用于选择性吸附小生物分子与生物大分子。
然而当前的吸收/净化方法受限于捕获单目标,而同时捕获多分子,正如在实际血液样本中经常出现的情况一样,仍具备挑战性。此外,大多数大体积吸附材料面临着与目标分子接触不充分的困境,而且缺乏血液清洁应用需要考虑的流体环境。而且通过吸附剂性质的变化来监测吸附状态和指示吸附平衡的研究也很少。因此具有高效率和自我报告能力的选择性移除多种血液中分子的新颖吸附平台是十分可取的。
鉴于先前的MIPs仅聚焦于单分子印迹,且在流体环境中的作用尚未得到完全证明。作者提出了一种分子印迹聚合物反蛋白石颗粒(molecular-imprinted polymer inverse opal particles, MIPIOPs)。
反蛋白石结构科普见此。
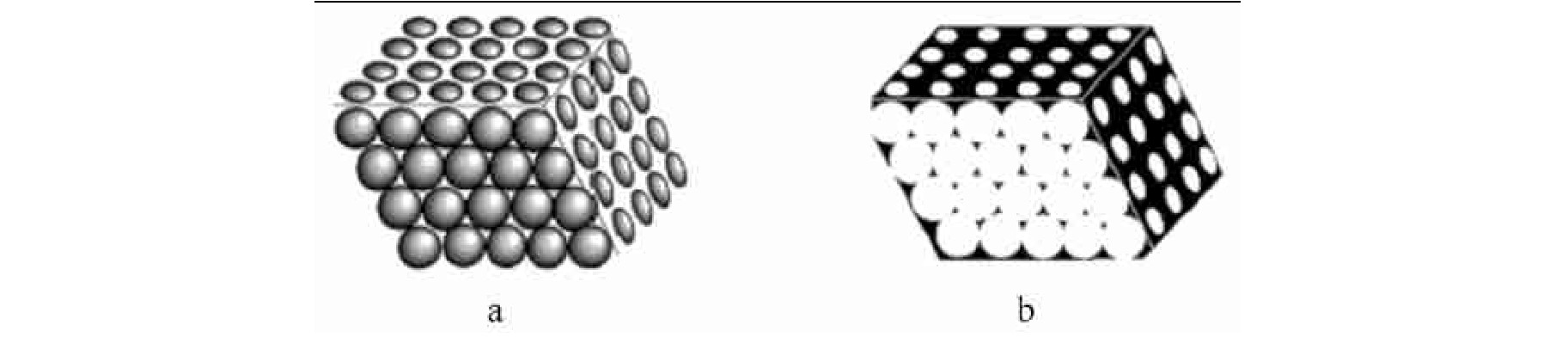
a为蛋白石结构,b为反蛋白石结构。
Figure 1.
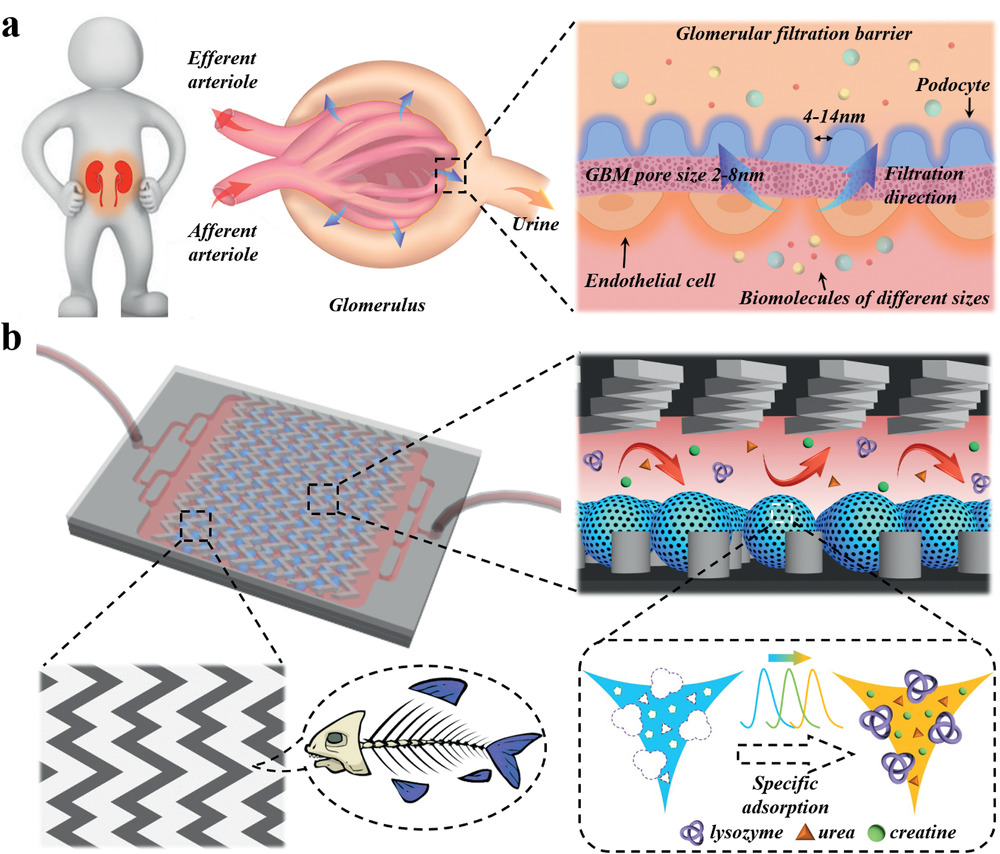
- (a)肾同时清除不同尺寸的生物分子的自我净化功能的示意图。不同尺寸的生物分子通过由内皮细胞层、肾小球基膜层和足细胞层形成的肾小球过滤屏障。
- (b)嵌入鱼骨微流控芯片的MIPIOPs用于多种血液生物分子(溶菌酶、尿素、肌酸)清除的机制。
Figure 2.

- (a)组合MIPIOPs的制作工艺示意图。
- (b-d)反射显微图像。
- (b)二氧化硅胶体晶体珠(SCCBs)是通过微流控乳化法制备,SCCBs表面的二氧化硅颗粒含有丰富的硅烷醇基团(带负电)因此可以通过静电作用吸附带正电的溶菌酶。
- (c)SCCBs表面的大分子溶菌酶可以作为印迹模版。在此,溶菌酶功能化的SCCBs在甲基丙烯酸酯明胶(methacrylate gelatin, GelMA)和聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯(polyethylene glycol diacrylate, PEGDA)的预凝胶混合物中膨胀,直到二氧化硅纳米颗粒之间的空隙完全填充。随后,预凝胶溶液在紫外光下聚合,SCCBs被氢氟酸蚀刻移除,印迹溶菌酶分子被PBS溶液冲走。此外包括尿素和肌酸的小分子被加入预凝胶溶液,在水凝胶骨架内部形成印迹。作者在预凝胶溶液中引入了丙烯酸,以提供足够的羧基。
- (d)结果产生的MIPIOPs拥有逐级的多孔结构,其中包括由印迹分子产生的小空洞和反蛋白石骨架产生的大空隙,具有多个结合位点。
- (e-g)扫描电镜图像显示三个阶段的MIPIOPs具有周期有序结构。
Figure 3.

- (a-c)通过紫外可见光谱测定的溶菌酶(a)、尿素(b)和肌酸(c)的沉浸时间和吸收值的函数关系。在约1小时时达到平衡,显示印迹的洞已经饱和。
- (d)对不同浓度的尿素和肌酸的吸附能力。因为生物分子在预凝胶溶液中的溶解度,最大浓度被限制在15 wt%。
- (e)不同浓度的丙烯酸下,三种分子的吸附度。丙烯酸用于给水凝胶骨架提供丰富的羧基基团。
- (f)两种不同的MIPIOPs对各自的印迹分子的特异性吸附能力。羧基在水凝胶骨架上的吸附能力所产生的少量非特异性吸附可以忽略不计。
血液中的尿素浓度是广泛使用的肾病检测指标。然而单一指示剂在复杂肾病诊断中不够敏感,因此血清中溶菌酶和肌酐浓度有助于反映人体健康状态。
辅助材料中某图:Zeta电位是对颗粒之间相互排斥或吸引力的强度的度量。
Figure 4.
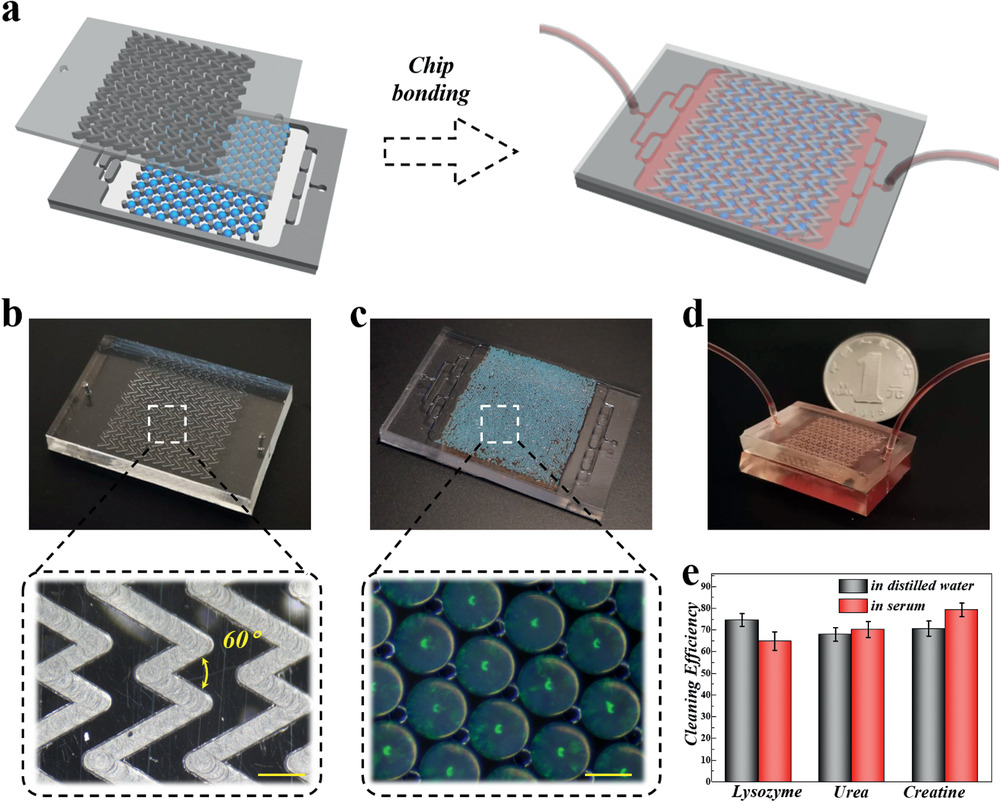
- (a)双层微流控芯片的制作过程示意图。底层为微室,顶层为鱼骨形混合器。
- (b)微流控芯片顶层的光学图像和鱼骨状微巢结构的细节。
- (c)微流控芯片底层的光学图像和由微柱图案组成的嵌有MIPIOPs的微室的细节。
- (d)整合了全部MIPIOPs的鱼骨状微流控芯片的光学图像。
- (e)微流控平台上在蒸馏水和血清中的三种分子的清洁效率。证明了该平台具有纯化临床血样的能力。
Figure 5.

- (a)鱼骨状微通道中的湍流形成的数值模拟。结果显示:鱼骨状通道产生了混沌对流,将改善平台的混合和吸附效率。
- (b)鱼骨状微流通道垂直截面的速度流线。
- (c-e)使用MIPIOPs和集成MIPIOPs的微流控芯片反复吸附后,溶菌酶(c)、肌酸(d)和尿素(e)的清洁效率曲线图。表明了集成MIPIOPs的微流控芯片比仅用MIPIOPs拥有更高的效率。
鱼骨状芯片论文祖师。
Figure 6.

- (a)MIPIOPs在不同浓度的靶分子溶菌酶作用下的光学响应。当溶菌酶浓度从0—1 mg mL-1时,红移的最大值为40 nm。
- (b)MIPIOPs对不同浓度的肌酸、溶菌酶和尿素溶液的反应的布拉格位移图。
- (c)孵育在不同浓度的溶菌酶的的MIPIOPs的布拉格衍射峰位移直方图。显示了MIPIOPs在水中和血样(血清)中具有相似的趋势。
- (d)溶菌酶吸收前后的MIPIOPs的反射显微图像和反射光谱。绿色的虚线和实线表示水中测得的溶菌酶吸收前后的反射光谱。红色描述了血清中相同的测试。意味着MIPIOPs可以直接用于血清,在临床肾病诊断中有潜在应用。
光子带隙(photonic band gap, PBG):光子晶体的特殊周期性结构,使得其对特定波长或波段的光子具有禁阻作用,形成光子带隙,类似半导体中的电子能带,将光子晶体中的光子带隙称为光子禁带。
由此将产生MIPIOPs的结构颜色与特征性反射峰,其主要反射峰位置λ可以通过布拉格方程计算:
$$
\lambda=1.633dn_{average}
$$
其中,d代表相邻反蛋白石空隙距离,naverage代表平均折射系数。当水凝胶溶液填充SCCBs的空隙和SCCBs模版被蚀刻时,混合分子印迹水凝胶的SCCBs和MIPIOPs的平均折射系数改变,从而导致反射峰位置的移动。如图2b-d所示,三组粒子显示出不同颜色。同时,通过简单地改变二氧化硅纳米颗粒的直径,可以制备出具有不同结构颜色的MIPIOPs,也改变了空隙的大小。此外,吸收过程中,靶分子与含印迹水凝胶框架上填充有水的纳米空隙结合,由于靶分子的折射指数(nurea=1.62、ncreatine=1.44、nlysozyme=1.37)均高于水(nwater=1.33),因此分子识别过程最终导致naverage的增加,即MIPIOPs颜色的红移。
Conclusion
作者对可扩展性进行了评估,可以将多个微流控芯片通过平行或堆叠以容纳更多MIPIOPs,进而适应于临床透析。相比于商业血液透析技术一次需要消耗8—10 L透析液,作者的平台具有可扩展性优势。
总而言之,作者报道了一种新颖的整合进鱼骨状微混合器的分子印迹反蛋白石颗粒,用于高效、同时吸附多种生物分子。
Reference
Chen H, Bian F, Sun L, et al. Hierarchically Molecular Imprinted Porous Particles for Biomimetic Kidney Cleaning[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(52): 2005394.



